W dzisiejszym trzecim odcinku na temat interfejsu użytkownika w aspektach layout’u, nawigacji, komend i kontrolek.
Z najnowszą wersją dokumentacji dostajemy precyzyjnie opisane typowe układy elementów na stronie aplikacji, z marginesami, nagłówkiem i główną zawartością. Kontrolka Page w JS ma zdefiniowane metody wywoływane w odpowiednich momentach cyklu życia strony. Przyciski komend w pasku aplikacji w JS reprezentowane są przez kontrolki AppBarCommand. Mamy udokumentowane zalecenia do sposobu umieszczania pasków i kółka postępu w zależności od układu sąsiadujących kontrolek i rodzaju okna czy komponentu. Omówione są różne sposoby nawigacji w kontrolce FlipView (nawigacja do przodu i wstecz lub pasek pokazujący aktualny element na tle innych i pozwalający na bezpośrednią nawigację do wskazanego elementu) oraz jej przeznaczenie (dla niedużych kolekcji) Możemy także dowiedzieć się, jak w szczegółach stylować wszystkie elementy kontrolki ListView włączając w to scenariusz z grupowaniem. Kontrolka SemanticZoom w JS obsługuje kontrolki implementujące interfejs IZoomable.
JS
Layout, navigation, commands
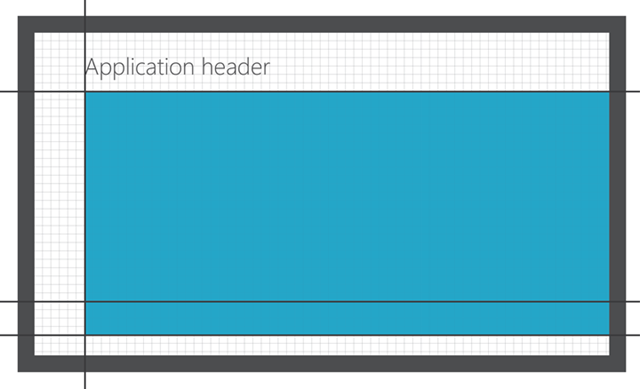
Page header
The baseline of the page header should be 5 units, or 100 pixels from the top. The left margin for the page header is 6 units, or 120 pixels. The Windows 8 page header is SegoeUI Stylistic Set 20, light weight.
Content region
The content region has a top margin of 7 units, or 140 pixels. The left margin is 6 units, or 120 pixels. The bottom margin is flexible. For horizontally panning content, it should be no more than 6.5 units (130 pixels), and no less than 2.5 units (50 pixels). For vertically panning content, the top and left margins remain the same. There is no specified bottom margin because the content scrolls off the screen.
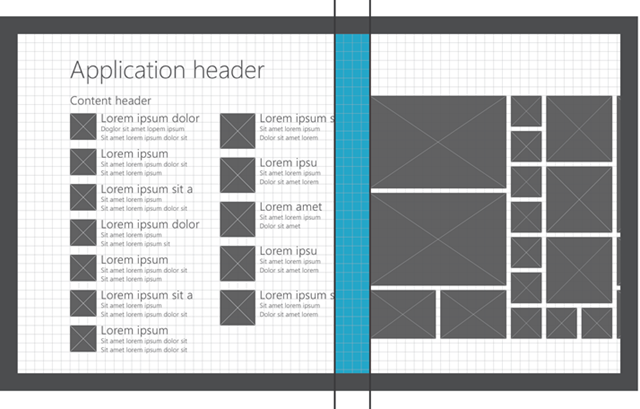
Horizontal padding values
Horizontal padding between content items varies depending on the items. Hard-edged items (like images and user tiles) have 2 sub-units, or 10 pixels, of padding between the tile and accompanying text. Lists have 2 units or 40 pixels of padding between columns. Hard-edged items have 2 sub-units, or 10 pixels, of padding between columns.
Vertical padding values
Vertical padding between content items also varies depending on the types of items. Tile and text lists have 1 unit, or 20 pixels of vertical padding between items in a row. Hard-edged objects have 2 sub-units, or 10 pixels, of padding between items in a row.
Horizontal padding between groups
The padding between groups is 4 units, or 80 pixels. This padding is generous to allow enough separation to easily distinguish one group from the next when the user is panning.
Guidelines for scaling to pixel density
If your application is a JavaScript app and you have a remote web image, use the CSS @media min-resolution media query with a background-image to replace images at runtime.
@media all and (max-resolution: 134dpi){ /* Load 100% image when scaled by 100% */ .imageBackground { background-image: url('http://www.fabrikam.com/foo.png?s=100'); }}
If your application loads user images from the file system, you should use the File Access Thumbnail API which automatically retrieves a thumbnail for files on the file system that corresponds to the current scale.
If your application is loading images at runtime using code, use the Windows Runtime API to determine the scale and manually load images based upon scale percentage.
You should ensure to specify a width and height on images instead of using auto sizing for images to prevent layouts from changing when larger images are loaded.
Navigating
Microsoft Visual Studio 11 Express Beta for Windows 8 provides several new project templates that can make managing navigation easier. The Grid Application, Split Application, and Navigation Application templates provide a navigation control, called PageControlNavigator, that you can use to navigate between different Page controls.
- Add > New Item.
- Select HTML Page Control
The Page control includes a set of predefined functions that get called automatically, in a predefined order. The Page item templates provide a ready and an updateLayout function for you.
The PageControlNavigator calls the updateLayout function when the app's view state changes. It's called when the app switches between portrait, snapped, full screen, and filled view states.
The ready function is called when the page's DOM has been loaded, controls are activated, and the page has been loaded into the main DOM. The Page control supports additional functions for the page lifecycle.
Call the preventDefault method to prevent the default link behavior.
function linkClickEventHandler(eventInfo) { eventInfo.preventDefault(); }
With the "ms-https-connections-only" meta element value you can prevent your Metro style app using JavaScript from using HTTP connections for navigation or other non-media web content retrievals. When you set this meta element's content attribute to "true", HTTP navigation and non-media web content retrievals will fail.
Controls
If you're adding your control to a Page control, use the Page control's ready function to attach your event handlers. If you're adding the control to your own custom HTML and JavaScript files, handle the DOMContentLoaded event and use it to call WinJS.UI.processAll.
- If you added the control to your app's home page (which is usually the default.html file), add a call to WinJS.UI.processAll in your onactivated event handler, as shown in the previous example.
- If you added the control to a Page control, you don't need to add a call to WinJS.UI.processAll because the Page control does that for you automatically.
- If you added the control to another page that is not your app's home page, handle the DOMContentLoaded event and use the handler to call WinJS.UI.processAll.
Just like with HTML controls, the preferred way to attach event listeners for a Windows Library for JavaScript control is to use the addEventListener function.
You can use only AppBarCommands in an app bar.
<div data-win-control="WinJS.UI.AppBar" data-win-options=""> <button data-win-control="WinJS.UI.AppBarCommand" data-win-options="{id:'cmdAdd',label:'Add',icon:'add',section:'global',tooltip:'Add item'}"> </button></div>
You can put any custom HTML in the app bar when specifying layout:'custom'.
<div data-win-control="WinJS.UI.AppBar" aria-label="Navigation Bar" data-win-options="{layout:'custom',placement:'top'}"> <header aria-label="Navigation bar" role="banner"> <button id="cmdBack" class="win-backbutton" aria-label="Back"></button> </header></div>
Do set the app bar's dismissal mode to sticky when displaying contextual commands. If you have contextual commands on an app bar, set the mode to sticky while that context exists and turn off the sticky mode when the context is no longer present (such as when a photo is deselected). In sticky mode, the bar will not automatically hide when the user interacts with the application. The bar stays visible while the user performs the actions. The user can still hide the bar by swiping the top or bottom edge of the screen, and they can show it again with an edge swipe.
Do design your app bar for snap and portrait view. Don't have more than ten commands on your app bar, because that will wrap to two lines for many users. Because labels are hidden by default in snapped and portrait view, use icons that are easily identifiable for your commands and provide tooltips for all of your commands.
Do use the bottom app bar for commands and the top app bar for navigation. Use the bottom app bar for commands that act on the current page. Use the top app bar for navigational elements that move the user to a different page. Do not put navigation on the bottom bar.
Don’t put login, logout, or other account management commands in the app bar. All account management commands, like login, logout, account settings, or create an account should go in a Settings flyout. If it's critical that the user logs in on a particular page, provide a button in the main app window to allow the user to log in.
Don't put clipboard commands for text on the app bar. Place Cut, Copy, and Paste commands in a context menu rather than in an app bar.
Don't show a context menu for the background of a page or for a large object. Instead, when you have commands that act on the background of a page or on a object that takes up the whole screen, use the app bar or add a command to your app's canvas to act on the page or object.
Order custom commands in the context menu by importance, with the most important commands at the bottom
Order clipboard commands in the standard Cut, Copy, Paste order and place them at the bottom of the menu
Adding selection controls
You can change the calendar that the DatePicker uses.
Select control modes
Flyout mode Use flyout mode when you need to conserve on-screen space and when users select only one option at a time. Flyout mode Select controls show only the currently selected item. Users must tap on the control to see other selectable items.
Flyout mode Use inline mode when you want the options to be visible all the time or when users can select more than one option at a time.
The select control has two modes: Drop-down list mode and List box mode.
- Determinate Progress Bar
- Indeterminate Progress Bar
- Indeterminate Progress Ring (Use this style for tasks that are not determinate and are modal (block user interaction). )
<progress id="determinateProgressBar" value="30" max="100"></progress>
<progress></progress>
<progress class="win-ring"></progress>
<label class="progressRingText"> <progress class="win-ring withText"></progress>Processing</label>
Show a single progress control for multiple active related tasks. For example, if the app downloads multiple photos, show a single progress control, instead of showing one for every photo.
In a dialog, an action occurs before you move to the next screen
Showing progress in an app window with right-aligned controls
Showing progress in an app window with left-aligned controls
Showing progress in a flyout
Use a flyout if activity can proceed in the background when the user dismisses the flyout by tapping outside it.
The contents of the tooltip can be text or an image but is not interactive.
Don't put interactive controls inside the tooltip.
FlipView
Important: Set the height and width of your FlipView. For a FlipView to render, you must specify its height with an absolute value.
There are two ways to create a template: you can use markup to define a WinJS.Binding.Template, or you can create a templating function.
Your template must be defined before you use it.
The FlipView control lets people flip through views or items one at a time. Flip buttons appear on mouse hover and let people flip to the next or previous item.
You can also add a context indicator control so users can jump directly to a particular item.
Use a FlipView control to:
- Flip between items in a small collection ( < 10) of related items
For example, in a shopping app, you might want to show several images of a product in a product details page. You can use the context indicator control for a small collection, but this is often not necessary.
- Flip between items in a medium-sized list (10 to 25 ) of related items
For example, in a real estate app, you might want to show a number of images of each house, showcasing the rooms and views. For these medium-sized lists, include a context indicator control, like a filmstrip of thumbnails, that lets users to jump to specific photos.
- Flip between views of an application
For example, an app launcher can have one view that shows a user's favorites in a grid and another that shows the favorites in a list. You can add a FlipView control to let users navigate from one view to another.
Don't use a FlipView control for large collections. The repetitive motion of flipping through each item becomes tedious for users. A ListView control is a better choice
The FlipView can display interactive content, such as a table of contents that jumps you to the selected image.
The FlipView exposes methods and events that allow you to create custom controls that give the user an idea of where current item is and alternative mechanisms for navigating the collection. The following image shows a set of styled radio buttons that are kept in sync with the FlipView via the pageselected and pagevisibilitychanged events.
Use a context indicator when the items in the collection don't provide enough contextual information to help users know where they are in the collection. A FlipView for days of the week would not need a context indicator, whereas a FlipView for product images would.
Tailor the indicator for the number of items and the specific scenario. For small collections, you can show the entire collection in the context indicator. For medium-sized collections, you might want to show only 5 at a time, for example. For purely visual collections, you might display thumbnails; for text-based collections, you might prefer to display the alphabet so users can jump to the right letter.
ListView
The ListView doesn't dynamically adjust its height to fit your content. For a ListView to render, you must specify an absolute value for its height. The Windows Library for JavaScript style sheets set the ListView control's height to 400px. But it's easy to specify your own height by overriding the default style with your own CSS.
The CSS classes you use with ListView include:
- win-listview
Specifies styles for the ListView itself.
- win-container
Specifies styles for a ListView or FlipView item container. Each item has its own container.
- win-progress
Specifies styles for the progress control that shows when the ListView is loading items.
The ListView supports margins on its left, top, and bottom sides, but you can't specify a margin for its right side. One workaround is to add an element that's as wide as the margin you want and set its style.visibility property to "none", then add the element to the right of the ListView.
You don't have to create your template styles from scratch. For a set of commonly-used templates and their corresponding CSS, see Item templates for list layouts and Item templates for grid layouts.
The ListView element has two layout modes: list and grid.
To use the list layout, set the layout property to WinJS.UI.ListLayout:
<div id="basicListView" data-win-control="WinJS.UI.ListView" data-win-options="{ itemDataSource : DataExample.itemList.dataSource, itemTemplate: select('#mediumListIconTextTemplate'), layout: {type: WinJS.UI.ListLayout}}"> </div>
To use the grid layout, set the layout property to WinJS.UI.GridLayout.
You can change the layout of a ListView at any time, even after you created it.
Here are the primary classes you use to style the ListView:
- win-listview: styles the entire ListView.
- win-viewport: styles the viewport. This is where the scrollbar is displayed if it's needed.
- win-surface: styles the scrollable area of the ListView. When the surface is bigger than the viewport, the viewport displays scrollbars.
Styling the entire ListView control
If you want to add a fixed background image to the ListView control that shows behind the items inside, or if you want to apply a border to the entire control, override the win-listview class. This example gives the ListView an image background and a red border.
.win-listview { background-image: url('../images/icecream.png'); border: 2px solid red; }
Styling the viewport based on its scrolling direction
You can use to the win-horizontal and win-vertical classes to apply styles to the ListView when it scrolls horizontally or vertically.
The next example removes the left margin when the ListView can scroll vertically. It's common to give the ListView a vertical orientation when the view state is snapped.
.win-listview .win-viewport.win-vertical { margin-left: 0px; }
Styling the entire scrollable area
To style the scrollable portion of the ListView, override the win-surface class. This example applies to the ListView a background image that scrolls when the user scrolls through items.
.win-listview .win-surface { background-image: url('../images/icecream.png'); }
Styling the loading progress indicator
The ListView displays a progress indicator while loading items. You can style this indicator by overriding the win-progress class. This example hides the progress indicator.
.win-listview .win-progress{ display: none;}
Styling items and groups
The ListView contains groups and items.
- Each group is contained in a group header, represented by the win-groupheader class.
- Each item is contained in an item container, represented by the win-container class.
Styling an item
There are two ways to style items in your ListView. You can apply styles to the item template, or you can override the win-container class. There's one thing that you must always do in your template, and that's set the size of your items. If you don't set the size of your items, you might not get the layout you want.
To set the size of your items:
-
If you're using a WinJS.Binding.Template, set the size of the WinJS.Binding.Template element's child
-
If you're using a templating function, set the width and height of whatever DOM element your function returns.
Styling the item container
To style the item's container, override the win-container class. This example adds a border and some padding to each item's container.
.win-listview .win-container{ border: 2px solid gray; padding: 5px; }
Styling the group header
To style the group header, override the win-groupheader class. This example adds a gray background to the group headers.
.win-listview .win-groupheader { background-color: #bfbfbf; }
Styling item interactions
Styling an item in the hover state
When the user moves the pointer over an item, the item enters the hover state. To change the style for an item in the hover state, use the hover pseudo-class. This example changes the background and the outline of a hovered item.
.win-container:hover { background-color: red; outline: orange solid 5px;}
Styling items that have focus
To style an item that has focus, use the win-focus class as a part of your style selector when styling the item container. To style the focus outline, use the win-focusedoutline class. This example changes the focused outline to a red, dashed line.
.focusExample.win-listview .win-focusedoutline { outline: red dashed 2px; }
Styling selected items
Override these classes to customize the appearance of selected items:
- win-selectionborder
Styles the border around a selected item.
- win-selectionbackground
Styles the background of selected items.
- win-selectionhint
Styles the selection hint, a second checkmark that appears behind the selected item. Swiping the item makes the selection hint visible.
- win-selectioncheckmark
The checkmark on a selected item.
- win-selectioncheckmarkbackground
The background of the checkmark on a selected item.
You can also add the win-selected class as part of your style selector to customize other components, such as the item container, when an item is selected.
Create a version of your data source that contains grouping info. If you're using a WinJS.Binding.List, you can call its createGrouped method to create a grouped version of the List. The createGrouped method takes 3 parameters:
- getGroupKey: a function that, given an item in the list, returns the group key that the item belongs to.
- getGroupData: a function that, given an item in the list, returns the title of the group that it belongs to.
- compareGroups: a function that compares two groups and returns a value less than zero if the first group is less than the second group, zero if the groups are the same, and a positive value if the first group is greater than the second group.
// Sorts the groups. function compareGroups(left, right) { return left.charCodeAt(0) - right.charCodeAt(0); } // Returns the group key that an item belongs to. function getGroupKey(dataItem) { return dataItem.title.toUpperCase().charAt(0); } // Returns the title for a group. function getGroupData(dataItem) { return { title: dataItem.title.toUpperCase().charAt(0) }; } // Create the groups for the ListView from the item data and the grouping functions var groupedItemsList = itemsList.createGrouped(getGroupKey, getGroupData, compareGroups);
Next, set the ListView control's groupDataSource property to the data source that contains the group data. You use the List object's groups property to obtain another List that contains the group information. To obtain an IListDataSource, you call myData.groupedItemsList.groups.dataSource.
<div id="groupedListView" data-win-control="WinJS.UI.ListView" data-win-options="{itemDataSource: myData.groupedItemsList.dataSource, groupDataSource: myData.groupedItemsList.groups.dataSource, layout: {type: WinJS.UI.GridLayout}}"></div>
<div id="groupedListView" data-win-control="WinJS.UI.ListView" data-win-options="{ itemDataSource: myData.groupedItemsList.dataSource, itemTemplate: select('#mediumListIconTextTemplate'), groupDataSource: myData.groupedItemsList.groups.dataSource, groupHeaderTemplate: select('#headerTemplate'), layout: {type: WinJS.UI.GridLayout}}" ></div>
SemanticZoom
To provide this zooming functionality, the SemanticZoom control uses two other controls: one to provide the zoomed-in view and one to provide the zoomed-out view.
These controls can be any two controls that implement the IZoomable interface. The Windows Library for JavaScript provides two controls that implement the IZoomable interface: ListView and FlipView.
Never expose the user to a view that is unrelated in scope to the one they are currently viewing. For example, a view presented as a photo album should never switch to a File Explorer folder view.
Do limit the number of pages (or screens) in the zoomed-out view to three. Semantic zooming enables a user to quickly jump to content. Introducing excessive panning destroys this benefit.
Don't use a SemanticZoom to navigate a hierarchy. Use the SemanticZoom to navigate within the current content efficiently. The SemanticZoom should never change the scope of the content. (For example, don't use the SemanticZoom to zoom in to and out of folders).
W przypadku C# razem z szablonami Visual Studio otrzymujemy kilka predefiniowanych klas - m.in LayoutAwarePage i RichTextColumns. Zewnętrzne linki otwieramy za pomocą asynchronicznej metody LaunchUriAsync. W przypadku kontrolek można dostrzec różnice w stosunku do JS – nie wszystkie wszędzie występują (np. Rating czy AppBarCommand tylko w JS), a często jedna kontrolka z JS odpowiada kilku kontrolkom z XAML - np. ListView (JS) –> ListView (XAML) + GridView(XAML) czy progress –> ProgressBar i ProgressRing. Kontrolki współpracujące z SemanticZoom w XAML muszą implementować interfejs ISemanticZoomInformation.
Należy zwrócić uwagę na ciekawe rozwiązanie w PasswordBox. Jak chcemy podejrzeć wpisywane hasło używamy przycisku w kontrolce po prawej stronie.
Z pewnością warto znać szczegół związany z kontrolką WebView – nic nad nią nie może być rysowane i sposób na obejście tego ograniczenia w przypadku paska aplikacji.
Dobrze też jest zapoznać się z predefiniowanymi szablonami dla elementów list na obu platformach i oszczędzić sobie pracy zyskując jednocześnie jeszcze większą unifikację z innymi aplikacjami Metro.
C#
Layout, navigation, commands
LayoutAwarePage .cs|.vb|.cpp|.h:
- is primarily used to listen for view state changed events (e.g. snapped, portrait, and filled state) and respond by switching the Visual State of the page. You can override this behavior to provide custom Visual State names and still use the event code provided in this file. For example, if the user sometimes has a different UI when the app is in the snapped orientation (e.g. user is logged in versus logged out), you could use two Visual State names corresponding to those different UI’s, but still use the same event code provided in this file.
- contains our default view model. For simplicity, we have created a property in this file that is a Dictionary mapping String to Object. This provides a very light-weight View Model that you can use for data binding in the various views. Feel free to use this ViewModel or provide your own and ignore this property.
- as each page has the same Go Back button, we provided the event handlers in this root type because they always have the same Navigation Service call.
RichTextColumns .cs|.vb|.cpp|.h
In the Grid Application, when viewing the Item Details, we wanted to show the entire text for a given item. This text is expected to flow vertically first in a fixed width column, and horizontally in as many columns as is necessary. This control provides that mechanism. Simply provide the content you want to have and then a template for each column and it will generate the required number of columns for your data on the fly.
We recommend you use these pre-defined styles for your XAML controls when possible because they look attractive, enable good usability, and are consistent with other Metro style apps. That said, when you feel you must override these styles, feel free to do so. But don't modify the styles directly in the StandardStyles.xaml file.
Tip: A fast way to apply styles to your controls is to right-click a control on the Visual Studio or Blend design surface and select Edit Style or Edit Template (depending on the control). You can then apply an existing style (like from the StandardStyles.xaml file) by selecting Apply Resource or define a new style by selecting Create Empty. If you create an empty style, you have the option to define it in the page, in the App.xaml file, or in a separate resource dictionary.
this.Frame.Navigate(typeof(BasicPage2));
The LayoutAwarePage class defines the methods GoBack and GoHome. The Back button on the page invokes the LayoutAwarePage.GoBack method and the Home button invokes the LayoutAwarePage.GoHome method.
You can specify that a page be cached by using the NavigationCacheMode property. In the constructor of BasicPage1, set NavigationCacheMode to Enabled.
To add a link to an external webpage.
In the Click event handler of the HyperlinkButton, call LaunchUriAsync with the Uri of the webpage that you want to link to.
private async void HyperlinkButton_Click_1(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e){ Uri uri = new Uri(@"http://www.bing.com"); bool success = await Windows.System.Launcher.LaunchUriAsync(uri);}
Your Metro style app can display an external webpage in a WebView, but you can't navigate from your top-level page to an external webpage.
Controls
A fast way to apply themes to your controls is to right-click on a control on the Visual Studio or Blend design surface and select Edit Theme or Edit Style (depending on the control you are right-clicking on). You can then apply an existing theme by selecting Apply Resource or define a new one by selecting Create Empty.
<Page.BottomAppBar> <AppBar Padding="10,0,10,0"> <Grid> <Button Click="GoHome" HorizontalAlignment="Left" IsEnabled="{Binding Frame.CanGoBack, ElementName=pageRoot}" Style="{StaticResource HomeAppBarButtonStyle}"/> <StackPanel Orientation="Horizontal" HorizontalAlignment="Right"> <Button IsEnabled="{Binding CanFlipPrevious}" Click="PreviousButton_Click" Style="{StaticResource PreviousAppBarButtonStyle}"/> <Button IsEnabled="{Binding CanFlipNext}" Click="NextButton_Click" Style="{StaticResource NextAppBarButtonStyle}"/> </StackPanel> </Grid> </AppBar> </Page.BottomAppBar>
<GridView/>
<ProgressRing IsActive="True"/>
The PasswordBox has a built-in button that the user can touch or click to display the password text. Here's the result of the user's action. When the user releases it, the password is automatically hidden again.
If you create your own custom text controls, you must implement TextPattern to use the touch keyboard.
Set a maximum length. If the backing data source doesn't allow a long input string, set the MaxLength property to limit the input and use a validation popup to let users know when they reach the limit.
Don't put another control right next to a password input box. The PasswordBox has a password reveal button for users to verify the passwords they have typed.
When you create a rich text box, provide styling buttons and implement their actions. (Metro style apps using C++, C#, or Visual Basic don't automatically provide these controls for you. )
Don’t disable spell checking just because the current spell checking engine doesn't support your app language. When the spell checker doesn't support a language, it doesn't do anything, so there's no harm in leaving the option on. Also, some users might use an Input Method Editor (IME) to enter another language into your app, and that language might be supported. For example, when building a Chinese app, although the spell checking engine doesn’t recognize Chinese now, don’t turn spell checking off. The user may switch to an English IME and type English into the app; if spell checking is enabled, the English will get spell checked.
The 256 named colors are based on the X11 color names from the CSS3 specification.
AppBar
You can respond to the app bar being opened or dismissed by handling the Opened and Closed events.
For example, this is useful if you need to open an app bar over a WebView control. Other content can't be rendered over the top of a WebView. When the app bar is opened over a WebView, the WebView covers the app bar.
You can work around this problem by handling the app bar's Opened and Closed events. When a user opens the app bar, you create a WebViewBrush and set the WebView as its source, then call the Redraw method which takes a visual snapshot of the WebView. You then use that brush to fill a Rectangle, and hide the WebView. The app bar renders its content over the top of the Rectangle. When the user closes the app bar, you no longer need the simulated WebView, so you can put things back the way they were in the Closed event handler.
<Page.BottomAppBar> <AppBar x:Name="bottomAppBar" Opened="AppBar_Opened" Closed="AppBar_Closed"> <Button Click="Refresh_Click" HorizontalAlignment="Right" Style="{StaticResource RefreshAppBarButtonStyle}"/> </AppBar> </Page.BottomAppBar> <Grid Background="{StaticResource ApplicationPageBackgroundBrush}"> <Border BorderBrush="Gray" BorderThickness="2" Margin="100,20,100,20"> <Grid> <WebView x:Name="contentView" Source="http://www.microsoft.com" /> <Rectangle x:Name="contentViewRect" /> </Grid> </Border> </Grid>
private void AppBar_Opened(object sender, object e) { WebViewBrush wvb = new WebViewBrush(); wvb.SourceName = "contentView"; wvb.Redraw(); contentView.Visibility = Windows.UI.Xaml.Visibility.Collapsed; contentViewRect.Fill = wvb; }
private void AppBar_Closed(object sender, object e) { contentView.Visibility = Windows.UI.Xaml.Visibility.Visible; contentViewRect.Fill = new SolidColorBrush(Windows.UI.Colors.Transparent); }
private void Refresh_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e) { contentView.Navigate(new Uri("http://www.microsoft.com")); bottomAppBar.IsOpen = false; }
- Use a list box when there are fewer then 10 items and the items are important enough to display prominently.
- Use a list box for multi-selection.
If there are fewer then 10 items and they should be prominently displayed, use a list box. If you have more than ten items and want to enable multi-selection, use a ListView.
Slider
Consider using a non-linear scale if the range of values is large and users will likely select values at one end of the range.
ListView & GridView
Predefiniowane szablony dla różnych rodzajów danych i scenariuszy
SemanticZoom
To provide this zooming functionality, the SemanticZoom control uses two other controls: one to provide the zoomed-in view and one to provide the zoomed-out view. These controls can be any two controls that implement the ISemanticZoomInformation interface. The XAML framework provides two controls that implement the ISemanticZoomInformation interface: ListView and GridView.
















Brak komentarzy:
Prześlij komentarz